KPI Examples & Templates Measure what matters the most and really impacts your success
DISCOVER THE RIGHT KPI EXAMPLES FOR YOUR BUSINESS
MUTE THE NOISE OF YOUR DATA TO FOCUS ON INSIGHTFUL AND IMPACTFUL KPI TEMPLATESA KPI or Key Performance Indicator is a measurement that evaluates the performance of a business activity. It measures a company’s success at reaching its operational and strategic goals on different performance aspects. KPIs can be high-level, monitoring the global performance of a business, or more low-level, focusing on processes or individual performance.
No matter which department you are in, KPIs are vital to grasp the status of your business and make the right calls. How can you tell which KPIs are relevant? Which is going to help you and which will cause a distraction?
KPIs help managers gauge the effectiveness of their functions, processes, campaigns, and actions. They are essential to ensure you are on track to reach organisational goals. All of the above is possible with datapine. We help you cut through the noise and see the actionable data you need. Control the act of accessing, visualising, and reporting with our first-class interface. Monitor your most significant KPIs in one place, obtain a comprehensive business overview, and make more informed decisions.
It isn’t always easy to find the right performance indicators that will fit each department or activity. The objective is always to determine those that communicate progress most meaningfully. We have identified the KPI examples that are most relevant for each department, specific industry or platform. Take advantage of our metric library and KPI templates to identify and visualise the metrics that are most important to your business area. Below you will find the links to over 350 visual KPI examples and templates with recommendations for action as well as relevant showcase dashboards.
Become a data wizard in less than 1 hour!
KPIS ARE JUST THE TIP OF THE ICEBERG
COMPARE YOUR RESULTS WITH YOUR GOALS AND ALIGN YOUR NEXT MOVE
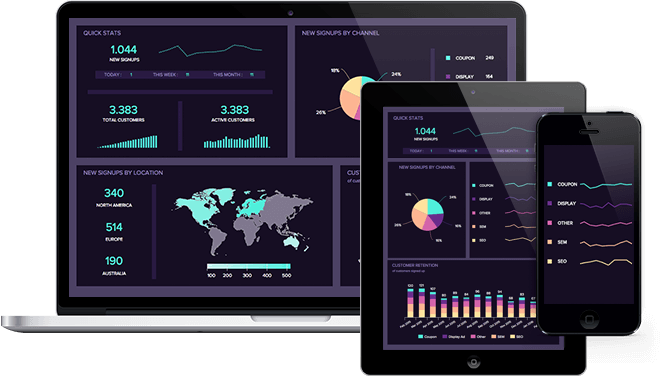
The KPI meaning in business is directly linked to potential success. These measurements ensure all relevant stakeholders (team members, managers, executives, etc.) are connected with general business goals and support them through different activities. They provide a general overview of a company’s performance in several areas and allow its users to quickly identify if an issue is happening and fix it immediately. And not just that, providing each team member with the right performance measurements can also help keep them accountable for their actions. For example, each sales representative can see their individual progress and optimise it to ensure they contribute to general departmental success.
Tracking the right KPIs is a huge step forward for any company - but why stop there? With datapine, identifying is just the first step. Explore, visualise, and efficiently communicate your insights across your company and induce more informed decisions enterprise wide.
But how do you choose the right ones for your specific needs? While there is a wide range of indicators to choose from, there are a few criteria you should follow to benefit from the best ones. We will cover this point in more detail later, but for now, it is important to keep in mind that your selection process should always be solely based on your core business goals. Your indicators should be actionable and help you measure the progress of your activities based on your general aims.
At this stage, you can also ask yourself a few critical questions that will map the role of each KPI. For example, what is the desired outcome, and how will it affect the organisation? Who is responsible for the outcome? How will you measure the progress of it? These should provide a few guidelines to ensure you extract the maximum potential of your KPI analysis process.
Once you have set up the right KPIs, datapine provides you with a comfortable, clean interface to keep an eye on them. Our dashboard software helps you eliminate the time consuming process of constantly having to log into databases, cross-referencing information, and pulling it out from third-party applications to ensure you are always up to date.
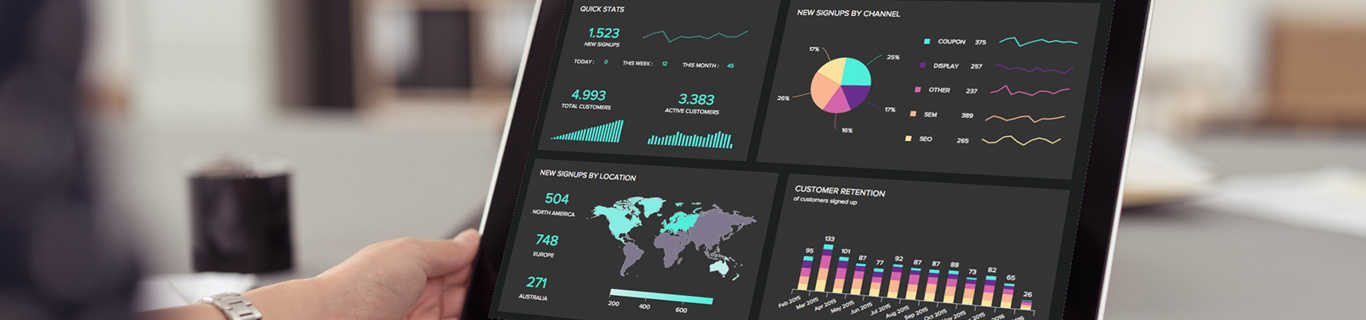
Thanks to modern KPI dashboards, your KPIs can be accessed in real-time, from anywhere, at any given time. All you need is an internet connection, and you are set to go. We ensure that you always have the most relevant figures in front of you whenever you need them. An enterprise-grade user management combined with several sharing concepts and scheduled automated reports empowers everyone in your company to constantly access relevant KPIs and make more informed decisions.
Why are KPIs So Important for modern business?
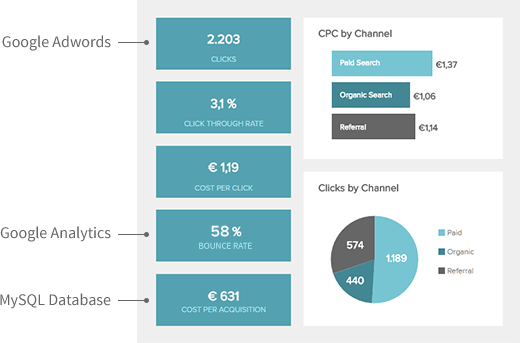
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are sets of quantifiable measures that can determine how effectively a company is achieving its key business objectives, thus evaluating its progress or success at reaching strategic and operational goals. Depending on which part of the business you would like to analyse, you have to select different KPIs. There are a wide range of indicators to choose from, and the process can be overwhelming. Just remember to pick only the ones that are directly related to your core business goals.
For example, if you want to track your company’s financial performance, you might use the return on equity ratio. If you want to analyse the performance of sales, you can use the lead conversion ratio. From this example, it is obvious that KPIs represent detailed specifications used to analyse the objectives of the organisation. It is essential to select the right KPI for a previously specified target in order to measure success. Since these indicators measure performance against a specific target, they help a company, department, or manager to instantly react to any events that might impact the business.
Which different Types of KPIs exist?
As mentioned, there are many types of KPIs, depending on the specific target and the best indicator to measure it. Some of them can be tracked for monthly progress, while others might be for yearly progress. Some of them might be linked to strategic goals, while others to operational ones. The broadest distinction is to separate the different kinds into nonfinancial and financial KPIs. The second refers to all indicators concerning the cash flow, debt, and assets of a company. For example, the profit margin, which measures the net profit in the percentage of revenue, or the current ratio, which is the ratio of current assets to current debts. The former refers to all indicators not directly related to the cash flow, debt, or assets of a company. A more specified distinction of KPI types is the following:
Quantitative vs Qualitative indicators: The first one can be expressed as a number, while the second one uses qualitative measures.
Lagging vs Leading indicators: Lagging indicates the source of success or failure of something that has already happened while leading indicators are used for forecasts.
Input vs Output indicators: The first one measures the resources consumed for a given output and the second the outcome of a process.
Process vs Actionable indicators: The former measures the efficiency or productivity of a specific business process, and the second one is mainly used by key decision-makers of a company to effect change.
Strategic vs Operational: Strategic ones are used to measure the long-term success of strategies like ROI, while operational ones are used to measure short-term performance like sales by region or transportation costs.
Another way is to distinguish the different types into departmental indicators, such as indicators for sales (for example sales growth), marketing (for example return on investment) or finances (for example current ratio) as we did in our KPI examples above. Check out our KPI templates for the different business departments to learn more.
As you’ve just seen, there are several ways to classify the different types of key performance indicators. The main distinction between all types is that they measure different performances, thus being only compatible with a specific target. The essence is to choose the right one, which measures the performance or success of your specific target the best. Thus, you have to know exactly what you would like to measure.
WHAT ARE THE KEY BENEFITS OF USING KPIS?
Let’s briefly explore some key benefits of using key performance indicators:
Informed decision-making: KPIs provide decision-makers with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions based on their current and historical performance. This way, they can build strategies based on accurate insights instead of pure intuition.
Increased transparency: Key performance indicators give businesses an objective view of how the different departments, teams, and areas perform. This knowledge allows for a level of transparency and accountability needed to succeed.
Increased productivity: When employees and other relevant stakeholders see their strategies are developing positively, they will be more motivated and engaged with the business’s success.
Lower costs: Strategies built based on intuition instead of factual data are at risk of finance failing and costing the company a lot of money. With the help of professional KPIs, businesses can build accurate strategies and ensure their budgets are spent smartly.
HOW TO PERFORM PROFESSIONAL KPI ANALYSIS?
After you’ve successfully identified the right KPIs for your business, it’s time to start the analysis process and generate actionable insights. Keep in mind that the value of the KPI analysis depends on the quality of the data as well as the skills of the analyst who is diving into the performance mix. datapine has a user-friendly interface that allows any user, without the need for technical knowledge, to generate KPIs with just a few clicks. Here we present some tips that can help in the process:
Create an interactive dashboard: Business dashboards are extremely useful when analysing KPIs since they enable you to visualise and interact with each of them through powerful filters and features that traditional analysis lack. During analysis, ask specific questions and dig deeper into the data; for example, if your dashboard visualises a map with the best-performing countries or regions, you can simply click to zoom, and display additional information, such as which cities, timeframes, or teams are responsible for success. That way, you can support any discussions that arise at the moment and incorporate additional findings that you can use for your future strategy development.
Set realistic and measurable targets: A fundamental step in efficiently performing KPI analysis is to set actionable targets to monitor development. Now, setting targets is not easy as you need to ensure they are not too high or too low but realistic to the organisation. Setting too high targets and quickly realising that all efforts are not helping in achieving them can be frustrating for your team. To avoid this, set targets that are align with your current performance and that you always readjust based on them. Another good practice is to divide them into long-term and short-term.
Compare different periods: Showing the development or decline in a certain performance indicator is a simple step to assist you in identifying if the bigger picture is improving or if you need additional adjustments. Connecting to this point, comparing different periods will also tell you how your performance has changed, allowing you to easily identify which actions caused those changes. For example, suppose you see that the number of sales contracts has declined in the past 3 months compared to the same period last year. In that case, you can examine if external factors have caused it (such as a pandemic) or internal ones (your sales team is reduced and you don’t have enough resources to fill the voids).
Incorporate intelligent alarms: Data alerts using modern technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence is another critical point to consider. KPI analysis has evolved from manual calculations into advanced algorithms that automatically notify the user when a KPI anomaly occurs. Predicting the next expected value of a data series is a feature of pattern recognition alerts that helps in achieving more accurate predictions, while the threshold alerts will activate as soon as the targets exceed or fall behind the pre-defined value. The intelligence behind these modern technologies will enable you to identify trends in your analysis, spot opportunities much faster, and eliminate tedious tasks of manual work.
Don’t focus just on the numbers: Numbers and software are the tools that will help you increase your productivity levels, save precious time, and ensure your information is up-to-date and visualised for easier comprehension. But numbers are not humans, and you always need to consider what kind of effect will your analysis cause on the human level. For example, if your leads are decreasing, you need to get yourself into your customers’ and teams’ shoes to identify why, not just blindly follow goals and objectives. If you see issues in your strategies, oftentimes, you need to adjust your approach, step away from the computer, and look beyond numbers.
Keep monitoring and evolving: Expanding on the point above, it is not enough to just choose a couple of KPIs and leave them there to measure your progress. On the contrary, your analysis process should be revisited regularly and optimised based on market, customer, and organisational changes. If this is not done regularly, it can throw away all the efforts invested. Therefore, it is important to make sure your KPIs are always up to date with the current requirements.
KPI analysis is designed to improve processes, ease repetitive work using modern KPI software, and stimulate a more efficient working environment. To help you even more, we have gathered the best practices that will stir your success and ensure sustainable development across the board.
What are common KPI Best Practices?
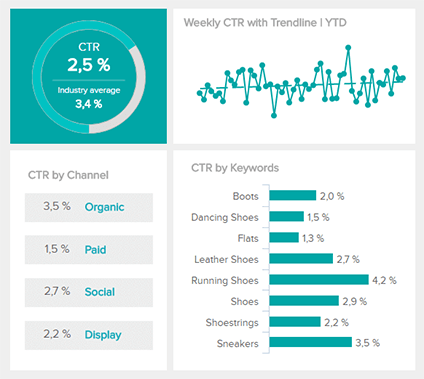
Choosing the right indicators for your specific target can be very difficult. But there are two main KPI best practices, that can help you to find the right one. A way to evaluate the relevance of a KPI is to use the SMARTER criteria (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-bound, Evaluate, Reevaluate). The long version of SMARTER means a specific objective, the measurability of the progress towards that goal, the realistic attainability of the target, the relevance of the target to your company, the timeframe for achieving the target and the continuous evaluation and reevaluation of the KPI.
The second KPI best practice is the six A´s (Aligned, Attainable, Acute, Accurate, Actionable, Alive). The six A´s mean that the indicators are aligned with your specific targets, the data, which is used for the indicators, can be easily attained, the indicators keep everyone informed (acute) about the current situation, the data used to obtain them is accurate, the insights in the business given by the indicator is actionable and the indicator should evolve with the business (alive).
KPI WORST PRACTICES YOU SHOULD AVOID
So far, we’ve covered what are KPIs, their different uses and best practices and useful tips to apply when building them. Before showing you our complete list of key performance indicators, we will go quickly through a few worst practices you should avoid at all costs when dealing with these measurements.
Avoid overloading: This worst practice starts with a simple statement: not because something can be measured it means that it should be measured. Many businesses make the mistake of monitoring many KPIs regardless of their relevance to the core strategy. The important thing to remember here is to pick up to 3 to 5 KPIs directly related to your goals. Picking too many can deviate from what actually matters and frustrate all your analytical efforts.
Choosing basic indicators: Expanding on the point above, you should avoid measuring KPIs that are too simple or basic. Your mantra should always be to choose strategy over simplicity. For example, while it is very easy to measure the number of new customers, you should consider if this indicator is providing any value to your goals or if you are just tracking it because it is easy to do it.
Collecting the same as everyone: We might sound like a broken record here, but these are tiny mistakes that can lead to higher consequences when successfully dealing with KPIs. Our third worst practice is to monitor the same things everyone else is monitoring. Just because an indicator is popular amongst other organisations, it doesn’t mean it will be successful for yours. Once again, keep in mind that everyone has a different strategy and KPI selection should be solely based on it.
Focusing only on the past: A couple of years ago, businesses only used past data to measure their performance and build their strategies. Today, thanks to the rise of modern BI tools, data can be analysed and visualised just a few seconds after it was first generated. For that reason, it would be a big mistake to measure your KPIs exclusively from a historical perspective. Using a mix of real-time and historical data can provide a more accurate picture of your performance, enabling you to make better strategic decisions in the long run.
Comparing yourself to others: We already mentioned the value and importance of setting KPI targets and goals in the previous section. However, if it’s not done correctly, it can end up harming your efforts. For instance, you should be careful when using industry or competitor benchmarks to evaluate your performance. It would be a great mistake to rely solely on industry values as each business works differently, and you can end up setting unrealistic targets that will ruin the morale of your team. We recommend using industry benchmarks as references but always mixing them with your current situation.
By avoiding these mistakes, you stand to achieve successful KPI management as well as gain a great advantage over your competitors. Now, without further ado, see our list of KPIs for different departments, functions, and platforms.
DESIGN TIPS FOR YOUR BUSINESS KPI EXAMPLES
Now that we know some of the best and worst practices for performing successful analysis, it is time to think about the design process. Rather you are generating KPI templates for your team or manager, designing them in an engaging and visually appealing way is a critical factor to the success of your analytical efforts. A well-designed indicator should strike a balance between well-presented data and simplicity. Let’s look at some key tips to correctly design your company KPI examples and templates!
Define your goals: Just like any other analytical process, before generating your KPIs, you should think about the audience and the general goal of the analysis. Doing so will help you pick the right chart to display the KPI and ensure the audience’s needs are covered, for example, by displaying a specific time period.
Keep it simple: When designing any type of data visualisation simplicity is key. While it might sound tempting to include 3D effects, icons, and other elements in your KPI samples, if they are not required, then they should not be included. Adding too many distracting elements to your design can make the data harder to understand for the audience, especially for non-technical users who struggle to grasp the information as it is.
Use text carefully: Text plays a crucial role in visualising your KPIs. The use of labels and legends helps the audience understand what the chart is talking about and any other extra details necessary for the analysis. That said, text should always be used wisely and with simplicity in mind. We recommend using a universal language for your labels, don’t make them too long to prevent overcrowding the visual, think carefully about placement, and include short explanations for too complex KPIs, in case the audience is not familiar with them.
Use colours wisely: As seen through our list of KPI examples presented above, these visuals are highly interactive and engaging to the eye. However, if you overdo it with the design, it can quickly become harder to understand. To prevent that from happening, keeping an eye on the way colours are used is a great practice. We recommend sticking to a couple of colours and using variations of the same to show different values. Using recognisable colours, such as green for positive results and red for negative ones, is also a great way to keep the audience engaged.
Following these simple tips will help you build successful KPI templates for multiple analytical scenarios. Just remember to keep simplicity as a top priority and you’ll be able to build engaging visuals that will skyrocket your business’s success.
COMPLETE LIST OF KPI EXAMPLES BY DEPARTMENT
Find hereafter a list of KPI examples specifically created to answer the needs of each department. All of them are compiled and visualised on professional KPI report templates that illustrate the data story every business possesses! Please click on the link of the specific department to learn more about the mentioned KPIs.
Management: Management KPIs give a strategic overview to top-managers and the C-level suite of the performance of certain parts of the business, so as to make data-driven decisions as soon as needed. Below you can find our top 8 key performance indicators examples for the management:
- 1) Customer Acquisition Costs
- 2) Customer Lifetime Value
- 3) Sales Target
- 4) Operating Expenses Ratio
- 5) Net Profit Margin Percentage
- 6) Return on Assets
- 7) Return on Equity
- 8) P/E Ratio
Finance: Financial KPIs track the performance of a business in its cash management, expenses, sales and profits. They allow you to stay on track with initial financial objectives. Below you can find our top 23 KPI examples for finances:
- 1) Gross Profit Margin Percentage
- 2) Operating Profit Margin Percentage
- 3) Operating Expenses Ratios
- 4) Fixed Operating Expenses
- 5) Variable Operating Expenses
- 6) Operating Expenses Development
- 7) Net Profit Margin Percentage
- 8) Working Capital
- 9) Current Ratio
- 10) Quick Ratio / Acid Test
- 11) Berry Ratio
- 12) Cash Conversion Cycle
- 13) Accounts Payable Turnover Ratio
- 14) Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
- 15) Vendor Payment Error Rate
- 16) Budget Variance
- 17) Actual vs Forecast Expenses
- 18) Actual vs Forecast Income
- 19) Return on Assets
- 20) Return on Equity
- 21) Economic Value Added
- 22) Employee Satisfaction
- 23) Payroll Headcount Ratio
Sales: Sales KPIs provide you with insights into your sales process and representatives. Tracking the pipeline health, lead generation, general activity and productivity, they are essential to driving sales forward. Below you can find our top 20 KPI examples for the sales team:
- 1) Sales Growth
- 2) Sales Target
- 3) Customer Acquisition Cost
- 4) ARPU
- 5) CLVT
- 6) Customer Churn Rate
- 7) Average Sales Cycle Length
- 8) Lead-to-Opportunity Ratio
- 9) Opportunity-to-Win Ratio
- 10) Lead Conversion Rate
- 11) Number of Sales Opportunities
- 12) Sales Opportunity Score
- 13) Average Purchase Value
- 14) Sales Volume by Country
- 15) Revenue & Profit per Product
- 16) Revenue per Sales Rep
- 17) Profit Margin per Sales Rep
- 18) NPS per Sales Rep
- 19) Upsell & Cross-Sell Rates
- 20) Incremental Sales by Campaign
Marketing: Marketing KPIs enable you to track your web performance in general and all the online campaigns you launch. They are important to give the big picture of all your online activities and determine an accurate marketing ROI. Below you can find our top 16 KPI examples for the marketing department:
- 1) Cost per Acquisition (CPA)
- 2) Cost per Lead
- 3) Sales Target & Growth
- 4) Average Order Value
- 5) Return on Investment (ROI)
- 6) CLTV
- 7) Website-Traffic-to-Lead Ratio
- 8) Lead-to-MQL Ratio
- 9) MQL-to-SQL Ratio
- 10) Goal Conversion Rates
- 11) Average Time to Conversion
- 12) Landing Page Conversion Rates
- 13) Cost-per-Click (CPC)
- 14) Bounce Rate
- 15) Engagement Rate
- 16) Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
Human Resources: HR KPIs are essential to a functional human resources team that aims at improving its recruitment processes, workplace well-being as well as monitoring overall employee performance. Below you can find our top 26 KPI examples for the human resources department:
- 1) Absenteeism Rate
- 2) Overtime Hours
- 3) Training Costs
- 4) Salary Cost By Department
- 5) Salary Cost Development By Department
- 6) Salary Cost Development By Country
- 7) Employee Productivity
- 8) Talent Satisfaction
- 9) Manager Feedback Score
- 10) Cost per Hire
- 11) Recruiting Conversion Rate
- 12) Time to Fill
- 13) Headcount Development
- 14) ) Average Job Tenurel
- 15) Talent Rating
- 16) Employee Turnover Rate
- 17) Talent Turnover Rate
- 18) Turnover Rate By Group
- 19) Dismissal Rate
- 20) Female to Male Ratio
- 21) Gender Diversity By Role
- 22) Gender Ratio By Department
- 23) Ethnicity Diversity
- 24) Recruitment Breakdown By Ethnicity
- 25) Part-Time Employees
- 26) Average Time Stay
Service & Support: Customer service KPIs are helpful to get a holistic view of your support department, agents, as well as a 360-degree customer view. They are crucial in the process of increasing customer satisfaction. Below you can find our top 18 KPI examples for customer service teams:
- 1) Average Response Time
- 2) First Call Resolution
- 3) Average Resolution Time
- 4) Cost Per Resolution
- 5) Customer Churn
- 6) Top Agents
- 7) Number of Issues
- 8) Total & Solved Tickets By Channel
- 9) Abandon Rate
- 10) Customer Satisfaction
- 11) Net Promoter Score
- 12) Customer Effort Score
- 13) Customer Retention
- 14) Net Retention
- 15) Service Level
- 16) Support Costs vs Revenue
- 17) Revenue Churn
- 18) MRR Growth Rate
Procurement: Procurement KPIs assist in the management of the procurement department as a whole, leading to more sustainable and improving processes. They regulate costs, savings, purchases, etc. Below you can find our top 18 KPI examples for the procurement department:
- 1) Compliance Rate
- 2) Number of Suppliers
- 3) Purchase Order Cycle Time
- 4) Purchase Price Variance
- 5) Purchase Order Coverage
- 6) Supplier Quality Rating
- 7) Supplier Availability
- 8) Supplier Defect Rate
- 9) Vendor Rejection Rate & Costs
- 10) Lead Time
- 11) Emergency Purchase Ratio
- 12) Purchases In Time & Budget
- 13) Cost of Purchase Order
- 14) Procurement Cost Reduction
- 15) Procurement Cost Avoidance
- 16) Spend Under Management
- 17) Maverick Spend
- 18) Procurement ROI
IT: IT KPIs maintain all the IT projects on track with their deliverables. Managing the constant flow of tickets and issues while keeping track of IT costs is the cornerstone of a well-functioning department. Below you can find our top 20 KPI examples for the IT department:
- 1) Total Tickets vs Open Tickets
- 2) Projects Delivered on Budget
- 3) Average Handle Time
- 4) New Developed Features
- 5) Number of Critical Bugs
- 6) Server Downtime
- 7) Backup Frequency
- 8) Cybersecurity Rating
- 9) Amount Of Intrusion Attempts
- 10) Mean Time To Detect
- 11) Mean Time To Repair
- 12) Phishing Test Success Rate
- 13) Unsolved Tickets Per Employee
- 14) Reopened Tickets
- 15) IT Support Employees per End Users
- 16) Accuracy of Estimates
- 17) IT ROI
- 18) IT Costs Break Down
- 19) IT Costs vs Revenue
- 20) Team Attrition Rate
COMPLETE LIST OF KPI TEMPLATES BY INDUSTRY
Likewise, you can find hereafter a list of examples of industry specific indicators designed to answer different needs. They are also all gathered and visualised on BI dashboards. Please click on the link of the specific industry to learn more about the mentioned KPIs.
Healthcare: Healthcare KPIs gather hospital and patient analytics to improve the facility management, the patient satisfaction levels as well as the staffing needs. It helps healthcare professionals run their hospital better. Below you can find our top 20 KPI examples for the healthcare industry.
- 1) Average Hospital Stay
- 2) Bed Occupancy Rate:
- 3) Medical Equipment Utilisation
- 4) Patient Drug Cost Per Stay
- 5) Treatment Costs
- 6) Operating Cash Flow
- 7) Net Profit Margin
- 8) Patient Room Turnover Rate
- 9) Patient Follow-up Rate
- 10) Hospital Readmission Rates
- 11) Patient Wait Time
- 12) Patient Satisfaction
- 13) Claims Denial Rate
- 14) Treatment Error Rate
- 15) Patient Mortality Rate
- 16) Staff-to-Patient Ratio
- 17) Cancelled/missed appointments
- 18) Patient Safety
- 19) ER Wait Time
- 20) Costs By Payer
Logistics: Logistics KPIs inform you on transportation processes, warehouse operations, supply chain management and other aspects involved in the optimisation of all the logistics operations. Below you can find our top 19 KPI templates for logistics:
- 1) Shipping Time
- 2) Order Accuracy
- 3) Picking Accuracy
- 4) Delivery Time
- 5) Pick & Pack Cycle Time
- 6) Order Cycle Time
- 7) Equipment Utilisation Rate
- 8) Trailer Utilisation Rate
- 9) Transportation Costs
- 10) Dwell Time
- 11) Inventory Carrying Costs
- 12) Warehousing Costs
- 13) Pick & Pack Costs
- 14) Operating Ratio
- 15) Use of Packing Material
- 16) Number of Shipments
- 17) Inventory Accuracy
- 18) Inventory Turnover
- 19) Inventory to Sales Ratio
Manufacturing: Manufacturing KPIs are a good asset when a business wants to optimise its production quality and manage the incurred costs efficiently. Below you can find our top 19 KPI templates for the manufacturing industry:
- 1) Production Volume
- 2) Production Downtime
- 3) Production Cost
- 4) OOE
- 5) OEE
- 6) TEEP
- 7) Capacity Utilisation
- 8) Throughput
- 9) First Pass Yield
- 10) Scrap Rate
- 11) Defect Density
- 12) Rate of Return
- 13) On-time Delivery
- 14) Right First Time
- 15) Asset Turnover
- 16) Unit Costs
- 17) Return on Assets
- 18) Maintenance Costs
- 19) Revenue Per Employee
Retail: In such a fast-moving industry, retail KPIs are crucial to any business that wants to identify and understand customer trends, enhance its stock management, lower the returns and ultimately increase sales profits. Below you can find our top 16 KPI templates for the retail industry:
- 1) Website Traffic/Foot Traffic
- 2) Average Transaction Size
- 3) Average Units per Customer
- 4) Total Volume of Sales
- 5) Sell-through Rate
- 6) Back Order Rate
- 7) Rate of Return
- 8) Customer Retention
- 9) Retail Conversion Rate
- 10) Total Orders
- 11) Total Sales by Region
- 12) Order Status
- 13) Perfect Order Rate
- 14) Return Reason
- 15) GMROI
- 16) Monthly Revenue Per Employee
Digital Media: Digital Media KPIs help online publishers assess their presence and the content they share. They are a big advantage to spot trends as they arise and answer their readers‘ expectations in a more customised way. Below you can find our top 9 KPI templates for the digital media industry:
- 1) Top Articles by Readers
- 2) Top Content Categories
- 3) Subscribers by Age and Gender
- 4) Average Clicks per Post
- 5) Average Shares per Post
- 6) New vs Lost Follower
- 7) Flesch Reading Ease
- 8) Average Comments per Article
- 9) Story Turnaround Time
FMCG: Fast-moving consumer goods KPIs are particular in the way that they are transversal and touch several departments, from procurement to supply chain so as to optimise any strategy to meet financial goals and product quality. Below you can find our top 10 KPI examples for the FMCG industry.
- 1) Out of Stock Rate (OOF)
- 2) Delivered On-Time & In-Full (OTIF)
- 3) Average Time To Sell
- 4) Sold Products Within Freshness Date
- 5) Cash-to-Cash Cycle Time
- 6) Supply Chain Costs
- 7) Supply Chain Costs vs Sales
- 8) Carrying Cost of Inventory
- 9) On-Shelf Availability
- 10) Margin by Product Category
Energy: Energy KPIs help suppliers understand and manage fast-changing market demands, optimise production costs and analyse consumption patterns. That enables them to maximise profitability in the long-run. Below you can find our top 8 KPI examples for the energy industry.
- 1) Power Cuts & Average Duration
- 2) Consumption by Sector
- 3) Total Shareholder Return
- 4) Operating Cash Flow
- 5) Production Costs
- 6) Availability Factor
- 7) Energy Production Distribution
- 8) Performance Ratio
Market Research: Market Research KPIs let you analyse and visualise your research results in a meaningful way, so as to present your studies to top management or clients effectively. Below you can find our top 14 KPI examples for the market research industry.
- 1) Unaided Brand Awareness
- 2) Aided Brand Awareness
- 3) Brand Image
- 4) Celebrity Analysis
- 5) Customers Age Groups
- 6) Customers By Gender
- 7) Customers By Education Level
- 8) Customers By Technology Adoption
- 9) Usage Intention
- 10) Purchase Intention
- 11) Willingness To Pay (WTP)
- 12) Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- 13) Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- 14) Customer Effort Score (CES)
COMPLETE LIST OF KPI TEMPLATES BY PLATFORM
Hereafter, you can find a list of KPI examples created to provide a solution for different platforms. They are compiled into a visual representation of the most important indicators of a successful data-story. Click on the link of the specific platform to learn what it can do for you and your business!
Facebook: Facebook KPIs gather content and advertising analytics to help social media professionals to optimise and maximise their social media strategy operations and results. Below you can find our top 10 KPI templates for Facebook:
- 1) Number of Fans
- 2) Follower Demographics
- 3) Page Views by Sources
- 4) Actions on Page
- 5) Reach by Post Type
- 6) Post Engagement Rate
- 7) Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
- 8) Ad Impressions & Frequency
- 9) CPM & CTR of Facebook Ads
- 10) Cost per Conversion
LinkedIn: LinkedIn KPIs let you analyse and identify the performance of a company or individual page profile, to determine the best possible combination of posting content, reaching to other professionals, and creating business opportunities. Below you can find our top 9 KPI examples for the LinkedIn network:
- 1) Followers’ Demographics
- 2) Number of Followers
- 3) Impressions & Reach
- 4) Engagement Rate
- 5) Company Update Stats
- 6) Viewer Information
- 7) Contact & Network Growth
- 8) Profile Views by Job Title
- 9) Post Views & Engagements
Twitter: Twitter KPIs inform you of the results of your set targets and indicate which performance is on track, and which needs to be optimised, leading to a sustainable social media strategy and operation. Below you can find our top 10 Twitter KPI examples for this social media platform:
- 1) Average Amount of Link Clicks
- 2) Average Engagement Rate
- 3) Average Amount of Impressions
- 4) Top 5 Tweets by Engagement
- 5) CPM of Twitter Ads
- 6) Results Rate of Twitter Ads
- 7) Cost per Result of Twitter Ads
- 8) Interests of Followers
- 9) Number of Followers
- 10) Hashtag Performance
YouTube: YouTube KPIs are crucial for the serious video story-teller, aiming to increase engagement, views, subscribers and overall performance of this channel. Below you can find our top 13 KPI examples for the YouTube platform:
- 1) Total Watch Time
- 2) Total Amount of Video Views
- 3) Viewer Retention
- 4) Video Engagement
- 5) Positive & Negative Comments
- 6) New & Lost Followers per Video
- 7) Number of Subscribers
- 8) Daily Active Users (DAU)
- 9) Traffic Source
- 10) Subscribers’ Demographics
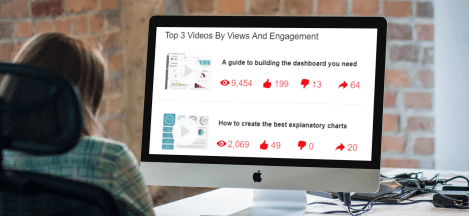
- 11) Top 5 Videos by Views
- 12) Revenue Per Mille
- 13) Playback-based CPM
Google Analytics: Google Analytics KPIs enable website operators to objectively monitor, analyse and optimise user behaviours on a sustainable level across the entire website. This is our top 14 KPI list for Google Analytics:
- 1) Sessions and Users
- 2) New and Returning Visitors
- 3) Bounce Rate
- 4) Goal Conversion Rate
- 5) Time on Page
- 6) Average Page Load Time
- 7) Bounce Rate by Browser
- 8) Organic vs Paid Sessions
- 9) Average Session Duration
- 10) Top 5 Search Queries
- 11) Users by Gender
- 12) Pages per Session
- 13) Best Pages by Gender
- 14) Top 10 Landing Pages
Google AdWords: Google AdWords KPIs primarily focus on the monitoring, visualisation, analysis and optimisation of any kind of Google Search Engine Advertising (SEA) campaigns. These are our top 11 indicators for Google AdWords:
- 1) Number of Clicks
- 2) Click-Through-Rate (CTR)
- 3) Quality Score
- 4) Cost-per-Click (CPC)
- 5) Ad Position
- 6) Conversion Rate
- 7) Cost per Conversion
- 8) Budget Attainment
- 9) Cost per Mille (CPM)
- 10) Impression Share
- 11) View-Through-Conversions
Salesforce: Salesforce KPIs help salespeople effectively manage all relevant, strategic and ongoing processes of their customer liaisons through Customer Relationship Management (CRM). These are our top 16 KPIs for Salesforce:
- 1) Lead Response Time
- 2) Follow-Up Contact Rate
- 3) Open Pipeline Value
- 4) Open Pipeline by Product Package
- 5) Pipeline Value Forecast
- 6) Average Contract Value
- 7) Annual Contractual Value
- 8) Average Sales Cycle Length
- 9) Sales Activity
- 10) Outbound-Calls
- 11) Outbound-Calls Contact Rate
- 12) Number of Demos
- 13) Total Amount of Inbound Leads
- 14) Lead-to-Opportunity Ratio
- 15) Opportunity-to-Win Ratio
- 16) Lead Conversion Rate
Zendesk: Zendesk KPIs enable companies to objectively monitor the quality of customer service and support while optimising all relevant customer interactions in an effective, data-driven way. These are our top 19 metrics for Zendesk:
- 1) Ticket-Status
- 2) First Response Time (FRT)
- 3) Average Resolution Time
- 4) Customer Satisfaction
- 5) Tickets by Types
- 6) Tickets by Channel
- 7) Top Agents
- 8) Average Answer Time
- 9) Unsuccessful Inbound Calls
- 10) Quality Rate
- 11) Average Leg Talk Time
- 12) First Contact Resolution Rate
- 13) Utilisation Rate
- 14) Net Promoter Score
- 15) Digital Assistant Engagement Rate
- 16) Digital Assistant NPS
- 17) Digital Assistant Referral Rate
- 18) Digital Assistant Resolution Rate
- 19) Article Suggestions CTR
Become a data wizard in less than 1 hour!